India is a land of many tounges.
India speaks different languages like Hindi, English, Bengali, Marathi, Telugu, Tamil, Gujarati, Urdu, Kannada, Odia, Malayalam, Punjabi, Assamese, and Sanskrit.
Each language will have a different Vocabulary. Accounting is also a kind of language that contains different terms which must be learned by everyone for a smooth understanding of Accounting concepts.
In this topic of “3 Accounting Terms with Examples” everyone should learn, we are going to discuss these 3 Accounting terms including Practical Methods with Rules of Debit & Credit. Before you learn it, we should remind a Zulu Proverb.
“ You can’t cross a River without getting Wet ”
– Zulu Proverb
The above quote can be applied in Accounting. One can’t learn Accounting perfectly without understanding these 3 basic and important Accounting terms of
- Account
- Debit &
- Credit
Also, you can learn what is “T account” is and its purpose?
When an account is to be Debited?
When an account is to be Credited?
And also the Rules for Debit & Credit can be understood, if you read this article 100%.
In the Ocean of Accounting vocabulary, these 3 words are of great importance. We (www.sracademyindia.com) decided to present in a Practical way to the Students & Entrepreneurs, Owners, and Businessmen who want to learn Accounting easily.
We are trying to make it a crystal and synopsis kind of explanation to understand practically this topic “What are debit and credit in accounting’. At the end, you can gain full and complete knowledge of 3 Accounting terms.
Let’s jump into the details..!!
Basket of Mangoes
- What is an Account?
- What is “T” Account?
- Purpose of Account
- What is “Debit” Meaning in Accounting
- What is “Credit” Meaning in Accounting
- 7 Debit and Credit rules with Examples
1. What is an Account?
To understand this, Tell me,
Did you go to the Bank anytime?
Yeah, Of course..!!
Do you have any Bank Account?
Yes, I have a State Bank of India (SBI) Personal Account. Few of you might have more than one account. Right..! That’s different.
Normally, Banks will Create a Personal Banking account for the Individuals that will be called a “Savings account”.
What a Personal bank account has?
A personal bank account shows all the transactions you make or operate through Bank. It may be either Cash deposits, Cash Withdrawals, Interest credits, EMI Payments, Expenses, Receipts, or any other transactions.
The bank account is an Account maintained by the Banker in which financial transactions between the Customer and the bank will be recorded. The consolidation of all these transactions will be called a “Bank Statement”.
From a banking perspective, an “Account” is a summary of all the transactions made by an individual for a particular period. The period may be for a day or a week or a month or a year etc., The banks will provide separate Bank accounts to the Individuals, Corporates, and Associations, and No single account matches the others.
In Accounting also, a business will have numerous transactions to record. It may be either Purchase transactions, Sales transactions, Capital investments, Asset Purchases, Payment of expenses, Receipt of Revenues, etc. including Bank transactions.
All these transactions cannot be remembered manually. To record all the similar types of transactions in a single place is called an “Account”.
The Account may be either Capital Account, Asset account, Expenses account or Income account, etc.,
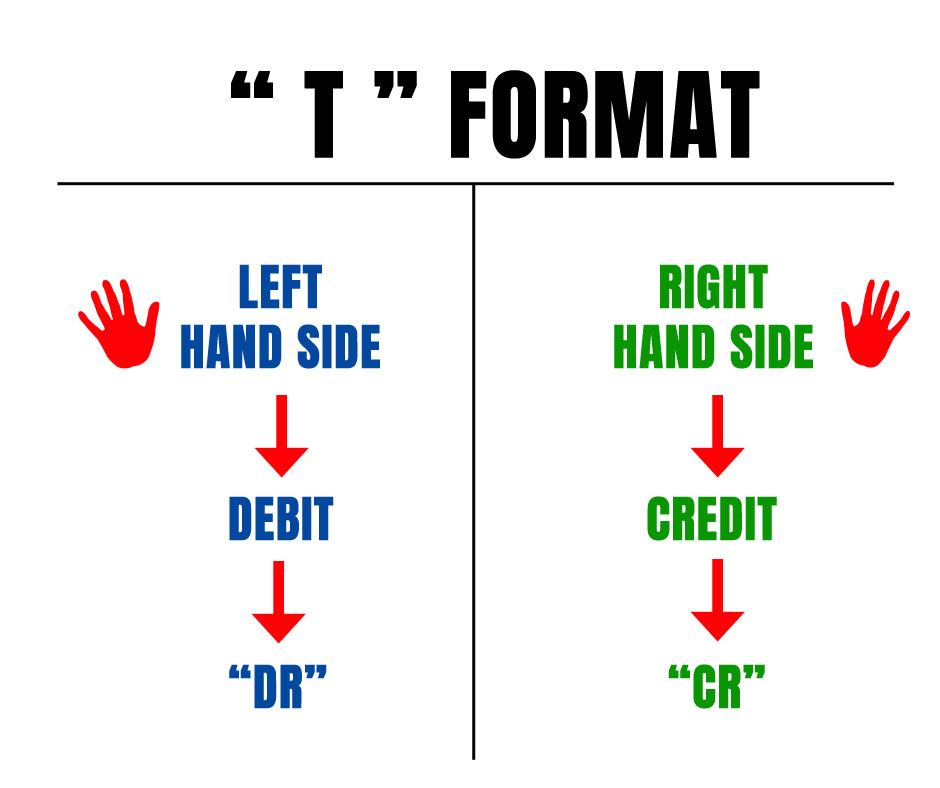
An “Account” is a system that sorts the financial transactions into records in a chronological manner. It is also a summary of records that tracks all the financial activities. This can be well understood by preparing the “Ledger accounts”. All the Ledgers will be prepared in “T” format.
2. What is “T” Account?
“T” Account is a shape adopted by the Accountants to summarize the transactions in a Pictorial representation using Debit & Credit.
Tip :
Debit means “Left-hand side”
Credit means “Right-hand side”
In India, If you go to the Vegetable market you will carry a large bag. All the veggies will be carried in that bag to home. It is a regular practice.
Tell me one thing, Will you put that entire bag into the refrigerator?
Of course, No…!!
Firstly, you will segregate veggies from large to small or by their type, then transfer them into a polythene cover or storage box and will store them in your refrigerator for future use.
Here, the fridge can be broadly seen as a “Business” and you have different packets covering Tomatoes, Brinjals, and Fruits, etc. which will be called a Tomatoes packet, Brinjals packet.
Here the Individual packet means “Individual account”.
Read: What are Financial Statements?
3. Purpose of Account
The better you are organized your refrigerator your cooking can be completed faster.
The purpose of having an account is to Track and organize the financial transactions of different accounts in a chronological manner. The better you are organized the financials can be prepared faster.
Example:
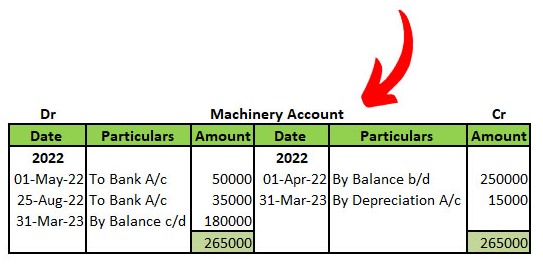
M/s X Ltd Company is having “Machinery” which is an asset for the business. To know whether we bought any other machinery or sold particular machinery or any expenses incurred towards repairs or depreciation etc can be known simply using an account called “Machinery account”.
How to Maintain it:
Initially, Accountants prepared these accounts by maintaining long physical books. But now a days you can maintain all these accounts in computerized software’s like Tally, Quick books, etc. which reduces both time & energy. In near future, accounting work may be replaced by Artificial Intelligence (AI).
4. Debit meaning in accounting
What is “Debit” or “Dr”?
As per the Oxford Dictionary, Debit means
“An entry recording a sum owed, listed on the left-hand side or column of an account”.
Debit can be denoted by “Dr” in short.
Yes..!!
“Debit” or “Debit entry” means an entry that is made on the “Left side of a Ledger account”.
As per the Double entry system of accounts “One account is to be debited and the other account is to be credited. For each entry of recording, the Total Debits and Credits must be equal.
Total Debits = Total Credits
Therefore, Trial Balance (TB) tallies.
5. Credit meaning in accounting
What is “Credit” or “Cr”?
The term “Credit” means
“An entry recording or listed on the “right-hand side of Ledger account ”.
Credit can be denoted by “Cr” in short.
To understand well into Debit and Credit, firstly understand the Rules for Debit & Credit.
Let’s begin.
6. Debit and Credit – 7 rules
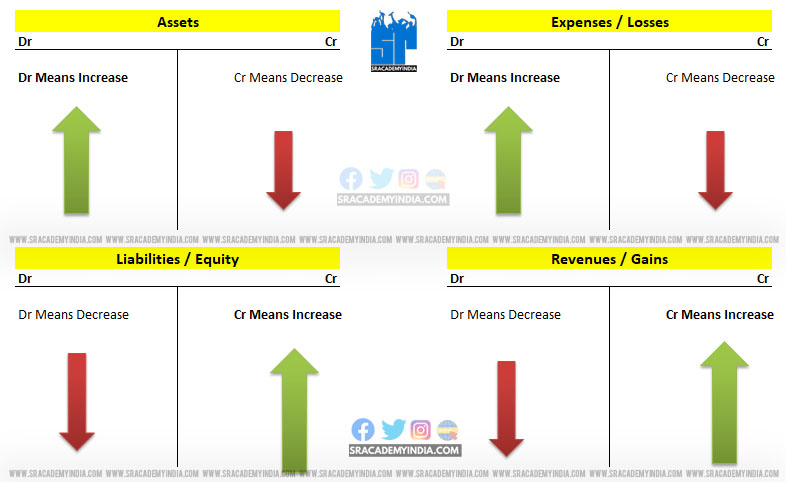
To understand the Debit and Credit rules, the Statement of Profit and Loss and the Balance sheet items are categorized into 7 accounts.
1. Assets account
2. Liabilities account
3. Equity account
4. Revenue account
5. Expense account
6. Gains
7. Losses

When an account is to be debited or credited is an individual case-to-case decision. One shall first assess and classify the type of account and it shall be accounted for accordingly.
The Simple Rules for Debit & Credit:
1. Asset Account:
For Asset account
* Dr means – Increase in Asset
Cr means – Decrease in Asset
Tip: Just remember only one side of the account for each account and the other side is just opposite or reverse (PS). Here * (Star) represents the recommended choice for remembering.
Example 1: M/s Money Ltd bought Machinery for Office of Rs.15,00,000/- from Mr.Bheem on 01.04.2022.
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Machinery a/c Dr | 15,00,000 | |
| To Accounts Payable a/c | 15,00,000 |
Logic: Office Machinery is an “Asset” and its balance is increasing. So it is “debited”. Simultaneously, on the other side, “Accounts Payable” is a Liability and it’s balance is Increasing, So it is credited. [ i.e. Increase in Asset]
2. Liability Account:
For Liability account
Dr means – Decrease in Liability
*Cr means – Increase in Liability
Example 2: M/s Money Ltd paid Rs.15,00,000/- to Mr. Bheem on 15.07.2022 towards Machinery purchased dated 01.01.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Accounts Payable a/c Dr | 15,00,000 | |
| To Bank a/c | 15,00,000 |
Logic: Accounts payable is a “Liability account” and it’s balance is decreasing, So it is Dedited. Bank is an Assets and its balance is decreasing, So it is credited [i.e. Decrease in Liability]
3. Equity account
For Equity account
Dr means – Decrease in Equity
*Cr means – Increase in Equity
Example 3: Capital brought into Business by the Owner of M/s Money Ltd Rs.50,00,000/- on 1.8.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Cash a/c Dr | 50,00,000 | |
| To Capital a/c | 50,00,000 |
Logic: Cash is an Asset and its balance is increasing. So it is debited. The “Capital account” is a “Liability account” and its balance is Increasing, So it is credited [ i.e. Increase in Equity]
4. Revenue account
For Revenue account
Dr means – Decrease in Revenue
*Cr means – Increase in Revenue
Example 4: Cash received by M/s Money Ltd for the completed services of Rs.50,000/- on 15.08.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Cash a/c Dr | 50,000 | |
| To Service Revenue a/c | 50,000 |
Logic: Cash is an Asset and it’s balance is increasing. So it is debited. The “Service Revenue” is the “Revenue account” and it’s balance is Increasing, So it is credited. [ i.e. Increase in Revenue]
Also Read: 8 Top reasons between Book Keeping Vs Accounting
5. Expenses account
For Expenses account
* Dr means – Increase in Expenses
Cr means – Decrease in Expenses
Example 5: Professional expenses paid by cheque of Rs.15,000/- on 1.09.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Professional expenses a/c Dr | 15,000 | |
| To Bank a/c | 15,000 |
Logic: Professional Expense is an Expense and its balance is increasing. So it is debited. Cash is an Assets and it’s balance is decreasing, So it is credited.. [ i.e. Increase in Expenses]
6. Gains
For Gains account
Dr means – Decrease in Gains
*Cr means – Increase in Gains
Example 6: A part of Equipment has been sold for Rs.1,50,000/- with a profit of Rs.65,000/- on 30.09.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Cash a/c Dr | 1,50,000 | |
| To Equipment a/c | 85,000 | |
| To Profit & Loss a/c | 65,000 |
Logic: Cash is an Asset and its balance is increasing. So it is debited and also “Equipment” is an Asset and it’s balance is reducing. So it is credited. The Profit from the sale of Equipment has been transferred to “Profit and Loss a/c” and its balance is Increasing, So it is credited. [ i.e. Increase in Gain / Profit]
7. Losses
For Losses account
* Dr means – Increase in Losses
Cr means – Decrease in Losses
Example 7: Printer sold for Rs.10,000/- with a Loss of Rs.4,000/- on 30.09.2022
The Journal entry is as follows:
| Cash a/c Dr | 10,000 | |
| Profit & Loss a/c Dr | 4,000 | |
| To Printer | 14,000 |
Logic: Cash is an Asset and its balance is increasing. So it is debited and also “Printer” is an Asset and its balance is reducing. So it is credited. The loss from the sale of Equipment has been transferred to “Profit and Loss a/c” and its balance is decreasing, So it is Debited. [ i.e. Increase in Loss]
Final Thoughts:
In simple, Golden rules of accounting + Simple rules for Debit & Credit = Journal Entries
One has to learn these accounting concepts perfectly to write journals with 100% accuracy.
I hope you liked our content.
Please do share if you like it. And, also give your feedback/suggestions to improve the content of “Debit and credit meaning” in the comments.