A 27 year old Bangalore based commerce student, Mr. Rohit’s family is financially unsound. As he wants to eradicate the financial burden by cracking a good job. So, he applied for a job position in a reputed company. Though he cleared the Written exam, but he is still worrying as the Interview is nearing.
He is wondering, what kind of questions i might get during the interview?
This is not only the situation of Mr. Rohit but also for many finance job aspirants like you.
Therefore, we are going to provide “18 Accounting basic Interview questions” which might helpful to crack the interview seamlessly. We provided the answers in an understandable manner. Therefore, please do not expect the answer to be in short.
Let’s Start..!!
1. Tell me about yours ?
Whatever the interview is..!!
Whether the interview is for a Government organization or for Private..!!
You will get this question at the beginning of the interview itself.
I call this question as a “Golden Question”
Simply, “Whatever the interview, the Interviewer will throw this question (i.e. Tell me about your’s) for you”
In any interview if you get this Question, you just blindly believe that you are Lucky..!!
Is this question really that lucky..!!
Yes..!! absolutely..
But the thing is, you should materialize it..
Don’t Worry guys..!!
I will tell you, How to answer this perfectly to win this interview..??
When an Interviewer throws this question at you, then, you will have at least 5-10 minutes of time in your hand to speak about your’s in the best elevating format.
In the movie Bahubali, before interval bang Anushka asks the stammered Prabhas a question.
Who are you? (i.e. Simply, Tell me about Your’s)
Then Kattappa takes the chance to speak about the heroicness of Bahubali.
But, for yourself, you are the Bahubali and the Kattappa.
So, Act yourself and prepare for a few sentences about your academics and experience (if any).
Do’s & Don’ts:
- Firstly, Introduce yourself and Speak about your academic qualifications in a enthusiastic manner. Like how hard your prepared (or) how smartly you studied.
But don’t be too lengthy. Be it simple and crisp.
(But don’t read out what your resume has during the interview)
Eg:
What a resume has:
– Qualified B.Com from Bangalore University with 75% marks in 2020.
What you should say:
“I’m Srivatsav, Qualified the Bachelor of Commerce from the prestigious Bangalore University. Due to my Handwork and dedication i was able to secure distinct marks / college first / state level rank”.
– Skip the year of passing.
Interviewer might feel drowsy if you say years for your academics.
Just keep in mind, if the interviewer asks you specifically then only you should speak about it.
- Do speak out your Qualifications as per descending order. i.e. Last qualified first.
- Never try to share your personal / financial problems with the interviewer. No one is ready to listen to your stories.
- How your past experience will help the company and how you are going to be useful to the organization .
- Also do speak out experience as per descending order. i.e. Latest experience first, if any.
- Don’t speak about your family, Caste, Religion, Political issues.
- Don’t make fake promises.
Eg: I will be in this company forever. - Never argue / Complaint.
- Be genuine while speaking.
Let’s see some of finance questions, you must be aware before going to an interview.
2. What is the difference between Journal & Ledger ?
Journal:
- A Journal records all the financial transactions of a business.
- All these transactions are to be recorded in a chronological manner. Every transaction recorded in a journal must be supported by a detailed narration. Narration explains the nature of such a transaction.
However, while passing these entries one must ensure that both the Debit and Credit totals should match.
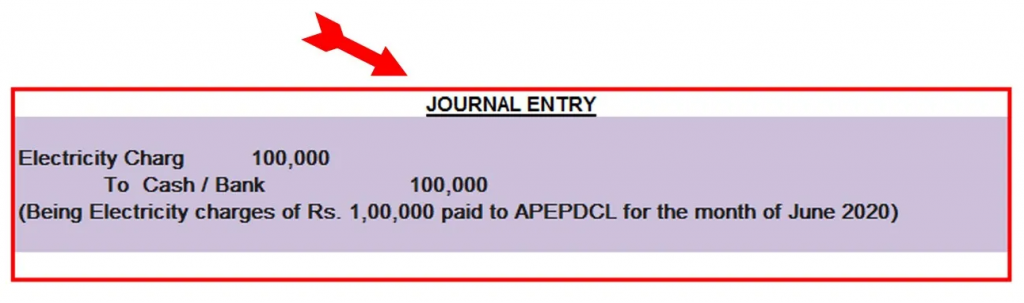
Let’s understand with the help of an example:
Example 1:
M/s Pipes Limited paid Electricity charges of Rs.1,00,000 to APEPDCL for the month of June 2020.
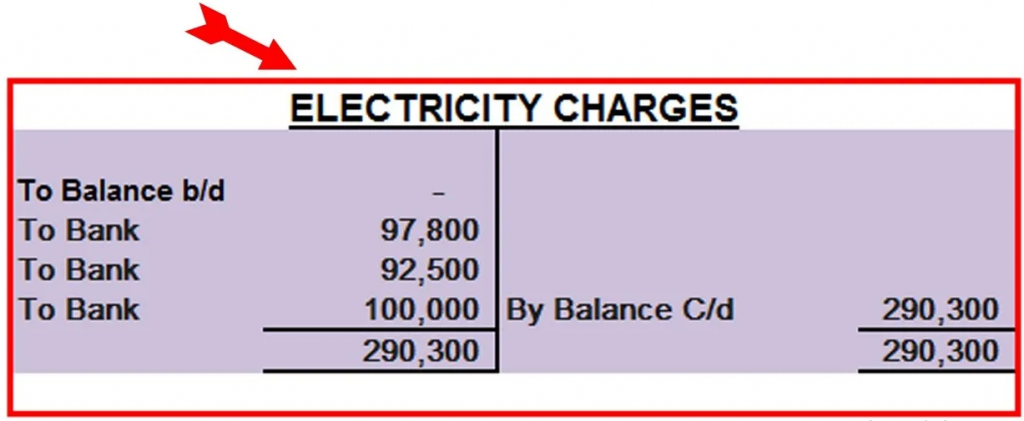
Ledger:
- A Ledger is a book where all the recorded journal transactions will be classified and posted.
Ledger basically gives you all the details of the transactions related to an Asset, Liability, Expense & Income in a particular period.
Ledger plays a key role in identifying all the transactions at one place, which are done by any entity in a particular period and also helps in quick decision making.
Ledgers are represented in “T” format which can be observed below:
Tips:
- In Journal, the transactions will not be recorded in classified manner whereas in Ledger the transactions will be recorded in a classified manner.
- Using Journal, it’s not possible to prepare Balance sheet easily but using Ledgers, this job can be done.
3. What is a Debit Note?
- When the business purchased the goods but those goods are not in satisfactory condition either due to Quality or any other reason, then, the purchaser of the goods (i.e. Buyer) will return the goods to the Supplier (i.e. Seller).
- This process of returning the goods by the purchaser to the supplier will be done through Debit Note.
- In simple, Dr notes means Purchase Returns.
The Dr note is a commercial document which will be issued by the Buyer to the Seller.
Eg: Mr. Rohan returned damaged pipes worth Rs.10,000/- to supplier of M/s Pipes Limited. Here, Mr.Rohan is a Buyer and M/s Pipes Limited is the Seller of Pipes. As the goods received by Mr. Rohan were in damaged condition, he shall issue a Dr Note on M/s Pipes Limited.
4. What is a Credit Note?
Cr note is contrary to the Dr Note.
It is from the viewpoint of Seller.
When the business sells the goods but those goods are not in satisfactory condition either due to Quality or Damage or any other reason to the Customer, then, the Customer of the goods will return the goods to the Seller.
Here, again the buyer issues the debit note and the Seller accepts it. And in return a Credit note will be prepared by the seller as an acknowledgement to the buyer.
- In simple, Cr notes means Sales Returns.
Credit note is a commercial document which will be issued by the Seller to the buyer.
5. What is the difference b/w Double entry & Single entry system of accounting
Double Entry System:
- Double entry system of recording is the scientific method of recording transactions in the books of accounts.
- Whenever you record any journal transaction, it will have an impact on at least 2 ledger accounts. One will be on the Debit side and the other will be on Credit side. The impact of transactions can be easily known on Assets, Liabilities, Incomes or Expenses.
This system of recording gives you a True and Fair view of accounts..
Eg: M/s Pipes Limited pays Rent of godown of Rs.5,000/-
As it is a business transaction, it will Increase “Rent A/c” and Decrease the “Bank Balance”.
The Debit amounts must be equal to Credit amounts.
Single Entry:
- In the Single entry system of recording, some transactions record only one side. Some transactions on the dual side and some transactions may not be recorded.
- It means that the Dr total and Cr total may or may not be equal.
This method of recording well suited to small business owners. It is an inefficient method of recording of transactions.
Therefore, this system of recording is not scientific and does not give you True and Fair view of accounts.
6. What is the difference between Account Receivables (AR) & Account Payables (AP)
Accounts Receivable:
A business may sells the goods or renders services either on Cash basis or Credit basis.
When the Seller sells the goods or renders the services on Cash basis, the seller immediately receives the Cash and there will be zero waiting time.
In case the Seller sells the goods or renders the services on Credit basis, the seller will not receive Cash immediately but will receive it in near future as agreed. Such receivable amount will be called as “Accounts Receivables”
Eg: On 01st April, M/s Pipes Limited sold pipes worth Rs.5,00,000/- to Mr. Agarwal, Mumbai on credit period of 90 days.
As the transaction is on credit basis, M/s Pipes Limited the seller of the goods shall receive cash before 29th Jun i.e. 90 Days. Otherwise interest may be charged for the delay.
Accounts Payable:
Similarly, a business may purchase goods or receive services either on Cash basis or Credit basis.
When the Buyer buys the goods or receives services on Cash basis, he immediately receives the Cash and there will be no waiting time.
In case the Buyer buys the goods or receives services on Credit basis, the Buyer will not pay Cash immediately but will pay it in near future as agreed. Such payable amount will be called as “Accounts Payable”
Eg: M/s Pipes Limited purchased Raw materials worth Rs.10,00,000/- from Mr. Rakesh, Punjab with a credit period of 45 days.
7. Why should Trial Balance be prepared?
- Trial balance is a statement which represents the balances of all ledgers at one place.
- It is prepared to ensure that all the debit and credit aspects of the transactions, on any particular day are matching with each other.
- Normally Trial balance will be prepared at the end of the period. The period may be either a Quarter or Half year or Full year i.e. Financial year.
3 reasons why Trial balance is prepared is
- To check the Arithmetical accuracy of the books of accounts.
- To check whether the Journal entries are properly posted to Ledger accounts and they are balanced as per double entry system of recording.
- To figure out any errors occurred in the books of accounts
Finally, the Dr side total must be equal to Cr side Total
[Dr side total = Cr side Total]
8. What is a Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)?
- Bank Reconciliation Statement is a statement whereby the Bank book transactions recorded by your business will be matched with the Bank statement recorded by the Bank.
- The process of identifying the difference between two is called “Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)”.
BRS helps to check the correctness of entries recorded by your business with the banker.
In case any adjustment entries are found, then, the necessary adjustment entries are to be made.
9. What is the difference b/w Tangible assets & Intangible assets ?
Tangible Assets:
Tangible assets are the assets which can be Seen, Touched and Felt. i.e. Physical substance.
These tangible assets may further classified into either Fixed assets or Current assets.
Eg: Plant & Machinery, Equipment, Cash, Furniture, Cars, Computers etc.,
Intangible Assets:
Intangible assets are the assets which cannot be Seen, Touched and Felt. i.e. No Physical substance.
Eg: Patents, Copyrights, Brans, Trade marks, Franchises, Goodwill etc.,
10. Who are Debtors ?
Debtor is simply a Borrower.
When a person sells goods (Seller) or renders services on credit basis, the person to whom the goods sold (i.e. Purchaser) will be liable to return the money to the seller. Till the payment is cleared, such a person will be called as a “Debtor”. The group of such persons will be called as “Debtors”.
Debtor is a person who owes money to the business.
Debtors will be treated as Assets under the “Current assets” section of the Balance Sheet.
Eg: Credit Sales
11. Who are Creditors ?
Creditor means simply a Lender.
When a person /business purchases the goods or receives the services on credit basis, the person from whom goods purchased it (i.e. Buyer) or received the services will be called as “Creditor”.
Creditor is a person to whom is liable to pay the amount i.e. to the supplier and the group of such persons will be called as “Creditors”.
Eg: Credit Purchases
12. What is Accounting Equation ?
- Accounting equation is the fundamental Accounting equation which derives the relationship between the total value of business Assets with Liabilities and Owner’s Equity.
- It is based on the Double entry system of accounting.
The accounting equation formula in broad is as follows.
Assets = Equity + Liabilities
For any Journal entry this accounting equation must be followed.
For each entry, either Assets on the left hand side may be increased or the equity and liabilities on the right hand side may be decreased or vice versa.
13. What is Working Capital ?
The excess of Current assets over Current liabilities is Working Capital.
I.e. Working Capital = Current Assets Less Current Liabilities.
It indicates Short-term position of the organization.
In simple, the Working capital will be used for Day-to-Day activities and also it represents the Liquidity of the business.
14. What are the Golden rules of Accounting?
Golden rules of accounting are:
- Debit What Comes In and Credit What Goes Out – Real Account
- Debit the Receiver and Credit the Giver – Personal Account
- Debit all Expenses and Losses and Credit all Incomes and Gains – Nominal Account
Read more : Golden rules of Accounting with examples
15. What is a compounded Journal entry ?
- A Journal entry which has more than one debit account or credit accounts will be called as “Compounded Journal Entry”.
- It may be either 2 Debit accounts or 2 Credit a/cs or both.
The combination will be as follows.
- One debit and 2 or more credits (or)
- One credit and 2 or more debits (or)
- 2 or more debits and credits
Eg:
Cash paid for the following
Stationery – Rs.1,000/-
Donations – Rs.3,000/-
Internet charges – Rs.2,500/-
Postage and telegram – Rs.750/-
The compounded journal entry is as follows:
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Stationery A/c Dr | 1,000 | |
| Donations A/c Dr | 3,000 | |
| Internet charges A/c Dr | 2,500 | |
| Postage and telegram A/c Dr | 750 | |
| To Cash a/c | 7,250 |
Here the Dr total = Cr total i.e. Rs.7,250/- only
16. Define Depreciation ?
If you use any asset, it’s value will be reduced over time due to wear and tear. I.e. Depreciation.
- In simple, Depreciation means Decrease in the value of an asset. It may arise either due to its usage or obsolescence or passage of time.
Eg: Motor Cars
17. What is Owner’s Equity ? Tell me any formula ?
- Equity means Owner’s capital (or) proprietor’s capital brought into the business in the form of Cash. It is called Owner’s Equity.
- If money is brought into the business by way of Shares, then it will be called as “Equity Share Capital”. While computing the Equity, Net income/ loss of the business should be taken into consideration.
- In Simple, Equity means “What the business owes to its Owners”.
- “Equity Formula is Total Assets minus Total Liabilities
18. What are the Financial Statements ?
To assess the financial performance of any entity, we need to interpret their financial statements properly. Financial statements gives lot of insights about the performance of an entity, which is the basis for the top management to take relevant decisions effectively.
The financial statements includes:
1. Profit and Loss account (To ascertain Profit or Loss)
2. Balance Sheet (To know What a Business Owns i.e. Assets & What a business Owes i.e. Liabilities)
3. Cash Flow Statements (To ascertain total Inflow and Outflow of funds)
4. Notes to accounts (Interpretation for the items considered in the accounts)
I hope you understood the “Accounting basic Interview questions” concept.
Please Comment “GOOD” if you like the article and it encourage us. Also share this article to your Finance related Friends & Family…
Thanks for reading..!!!