Hindus call it as “The Mahabharatha”
Christians call it as “The Bible”
Muslims call it as “The Quran”
Accountants call it as “Golden rules of Accounting”
Golden rules of accounting are:
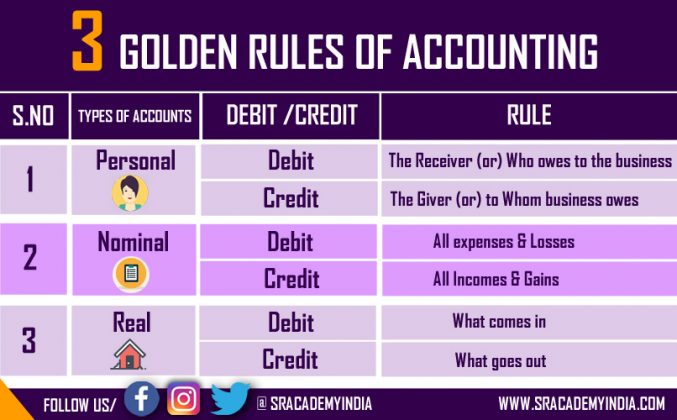
- Debit What Comes In and Credit What Goes Out – Real Account
- Debit the Receiver and Credit the Giver – Personal Account
- Debit all Expenses and Losses and Credit all Incomes and Gains – Nominal Account
Generally, every concept in the universe is defined by certain rules, which helps us in understanding the scope within which it operates.
Similarly, in Accounting also there are certain rules which define its scope and method of application in recording the financial transactions of any business. Simply, we call it “Rules of accounting” which is the backbone for accounting.
Then, why we are using the term “Golden rules of accounting“?
What is the significance of understanding these rules?
Are they really necessary while recording the journal entries?
Let’s understand the types of golden rules of accounting, its significance and the method of recording the journal entries with some practical examples.
Page Contents
- Introduction to golden rules of accounting
- Golden rules of accounting
- Practical examples of golden rules of accounting
Introduction to golden rules of accounting
Every business will have some goals. To achieve such goals, it should have a good strategy, ability, rules & principles in addition to the numerous other factors contributing to its success.
Whether you are an entrepreneur or an employee working for some one, to become successful in this dynamic world you need to understand the basic rules of accounting which govern every business and how these rules are to be applied in the process of accounting.
During my teaching, when I asked students to write a few basic accounting entries, most of the students were ended up with the wrong entries.
Some of the students even asked me like;
– I don’t know when to Debit an account & credit an account..!!
– My Sir told me that whatever comes to us is Debit & whatever goes out is Credit, Is it correct ?
The reason behind such lack of understanding is simple. Unfortunately, they are not aware of the basic rules which are the only guiding principles to record any financial transaction in accounting.
That is the reason we are calling it “Golden rules”, without which we cannot execute the process of journalizing (i.e. first step in the accounting process) effectively.
Golden Rules of Accounting
Let’s come to the point “Golden rules of accounting“.
As mentioned earlier, recording journal entries is the first step in the process of accounting; followed by the preparation of ledgers, Trial Balance, Profit & Loss account and finally Balance Sheet.
But, now with the entry of good accounting packages with a lot of features, recording the business transactions made easy and no need to go for a manual preparation from ledgers to Balance Sheet.
However, both in the traditional and modern accounting methods it has been mentioned on when to write on debit side of an account and when to write on a credit side of the account which can be discussed in further lessons.
Before you understand Golden rules of accounting, firstly you should learn about transactions.
Do you know what are Transactions in Accounting?
In a Business Organisations, numerous transactions will takes place.
For example, Purchase of goods from Suppliers, Payment of transport charges to a transport firm , Godown charges paid by Cash, Electricity, Security charges, Labour charges, Loss on Sale of Plant and Machinery etc., These are called as “Transactions”.
These transactions can be divided into 3 categories.
- Which are related to Individuals & Firms
- Transactions which related to Cash,Goods or Properties,Loans etc.,
- Transactions related to Expenses and Losses & Incomes and Gains.
Therefore, these transactions shall be accounted and classified based on rules of accounting which can also be called “Golden rules of Accounting.”
Golden rules of accounting are of 3 types.

1. Real Account
It means transactions relating to Properties & Assets. A business enterprise that owns it. Depending upon the physical existence or otherwise, it has been classified into
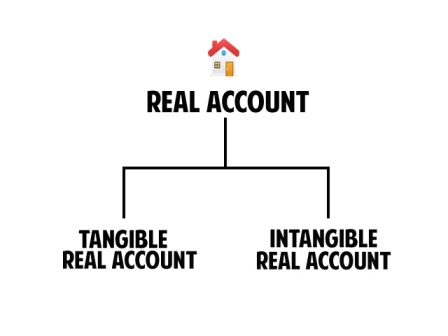
- Tangible:- It means assets which have
– Physical Existence
– Can be seen &
– Can be Touched
For example, Cash a/c, Motor car a/c, Building, Furniture, Machinery etc., - Intangible:- It means assets which have
– No physical existence
– Can‘t be touched &
– Can’t be seen
– But measured in terms of value & money.
For example, Goodwill, Patents, Trade marks, Copy rights etc.,
Rule:- Debit what comes in
Credit what goes out
2. Personal Account
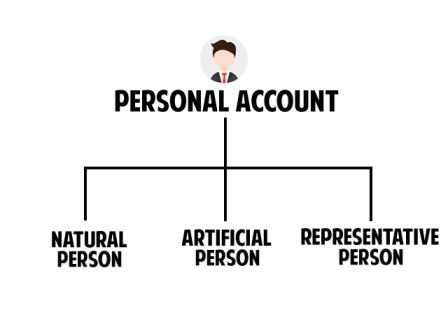
It means the transactions related to Persons. Persons may be either.
- Natural person :
Accounts which are related to individuals
For example, Mr Raju, Ms. Sita Mrs.Mamatha etc. - Artificial Person:
Accounts related to Firms (or) Companies (or) Societies etc.,
For example, Agarwal Industries, Rao & Co., HDFC Bank, General Insurance Corporation etc. - Representative Person:
Accounts which represent either a person or group of persons.
For example, When wages are payable to workers on daily basis, then cumulatively will be called as ” Wages Payable”.
Similar example is for Creditors.
Rule:– Debit the Receiver (or) the person who owes to the business
Eg: Credit Sales / Debtors
Credit the Giver (or) to Whom business owes
Eg: Credit Purchases / Creditors
3. Nominal Account

Nominal accounts means transactions relating to “Expenses or Losses” and “Incomes or Gains“.
For Example, — Salary account (Expense)
—Electricity account (Expense)
—Advertisement Account (Expense)
— Loss on Sale of Machinery (Loss)
— Income from Investment (Income)
— Gain on Sale of Car (Gain) etc.
Rule: Debit all expenses (or) Losses
Credit all Incomes (or) Gain
Practical Examples of Golden Rules of Accounting
Illustration 1 :-
Classify the following items into Personal, Nominal & Real Accounts
1. Sales 2. Capital
3. Mr. Surendra 4. Interest
5. Purchases 6. Rent
7. Bank 8. Sales Return
9. Electricity 10. Discount received
Solution:
1. Real 2. Personal
3. Personal account 4. Nominal
5. Real 6. Nominal
7. Real 8. Real
9. Nominal 10. Nominal
Illustration 2:-
Mr.Santosh Ltd & Co,a start up made the following transactions.
— Commenced Business with Capital
— Purchased goods for Cash
— Sold goods for Credit to Shakunthala Ltd
— Paid wages to Labour
— Paid salaries to Employees
— Bought a Car for Official Purpose and paid through SBI Bank.
— Paid Rent for Office.
Solution :-
Firstly, you must Identify the transactions to which accounts it will impacted.
Then, Classify them into different types of accounts.
| Transaction | Accounts Impacted | Type of Accounts |
| 1. | Bank a/c Capital a/c | Real Real |
| 2. | Purchases a/c Cash a/c | Nominal Real |
| 3. | Shakuntala Sales | Personal Nominal |
| 4. | Wages Cash | Nominal Real |
| 5. | Salaries Bank | Nominal Real |
| 6. | Car Bank/Loan | Real Real |
| 7. | Rent Cash | Nominal Real |
Now, we will apply the Golden rules to each of the transaction by making journal entries.
1. Mr. Santosh Started a business with capital
It is a transaction and
Capital to Santosh ltd is increased & also Bank balance is increased.
Now, apply Golden rules
- Debit what comes into the business. [Real Account]
Mr.Santosh brought capital into the business. So,Cash balance/Bank balance will be increased. So,Bank balance is to be debited. - Credit, the Giver or to whom business owes. [Personal Account]
Since the capital brought in by Mr.Santosh, X Ltd is in liability to pay the capital amount to Mr.Santosh. So, Mr.Santosh account is to be credited.So, the entry will be
Bank A/c Dr
To Mr. Santosh A/c Cr.
Note: You shall always pass entries from business point of view i.e., from Sanotsh ltd point of view.
Logic: Businesses needs recording of transactions which will be done by accountants. So, you shall always pass accounting entries from business point of view.
2. X Ltd purchased goods for Cash.
Due to purchase of goods, Stock balance will be increased &
Cash balance will be reduced after making cash payment.
Now, apply Golden rules,
- Debit, What comes into the business (Real Account)
Purchase of goods will increase in Stock, So purchases account is to be debited. - Credit,What goes out of the business.
Here, the cash balance is reduced. So cash account is to be credited. - So, the entry will be
Purchases A/c Dr
To Cash A/c Cr.
3. Sold goods for Credit to M/s Shakunthala Ltd
Due to Sale of goods, Stock balance will be decreased &
As the goods sold on credit, Shakuntala ltd become the Debtor of X Ltd. So, debtors will be increased.
Now, apply Golden rules
- Debit, the Receiver or Who owes to the business (Real Account)
As the goods are sold to Shakuntala Ltd, it owes money to X Ltd. So Debtors account is to be debited. - Credit,What goes out of the business.
Sale of goods will decrease in Stock, So Sales account is to be credited.
So, the entry will be
Debtors A/c Dr
To Sales A/c Cr.
4. Paid Wages to Labour
Payment of wages to labour is an expense. Due to payment of wages, expenses will be increased &
Cash balance will be reduced after making the payment.
- Debit, all the Expenses and Losses.
X Ltd paid wages to labour. So it is to be debited. - Credit,What goes out of the business.
Here, the cash balance is reduced. So cash account is to be credited.So, the entry will be
Wages A/c Dr
To Cash A/c Cr.
5. Paid Salaries to Employees
Payment of Salaries to employees is also an expense. Due to payment of Salaries, expenses will be increased &
Cash balance will be reduced after making the payment.
- Debit, all the Expenses and Losses.
X Ltd paid Salaries to employees. So it is to be debited. - Credit,What goes out of the business.
Here, the cash balance is reduced. So cash account is to be credited.So, the entry will be
Salaries A/c Dr
To Cash A/c Cr.
6. Bought a Car for Official Purpose and paid through SBI Bank
Purchase of Car is an asset to X Ltd. As the Car coming into the business, Car account is to be debited &
Cash/ Bank balance will be reduced after making cash payment.
- Debit, What comes into the business (Real Account)
Purchase of Car will increase in asset balance, So Car account is to be debited. - Credit,What goes out of the business.
Here, the SBI bank balance will be reduced. So Bank account is to be credited.So, the entry will be
Car A/c Dr
To SBI Bank A/c Cr.
Please do share if you like it. And, also give your feedback/suggestions to improve the content in the comments. Hit “Like” if you liked the article.
Thanks for reading 🙂
Disclaimer: Every effort has been made to avoid errors or omissions in this material. In spite of this, errors may creep in. Any mistake, error or discrepancy noted may be brought to our notice which shall be taken care of in the next edition. In no event the author or the website shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from or arising out of or in connection with the use of this information.

Simple explanation without using any financial jargons
Thank you Hari garu 🙂