“Life is like an Equation.
The future is unknown until you Solve it..”
– Ephraim Jaji
Similarly in Accounting also, there is an equation which is called an “Accounting Equation”. In this topic of “Accounting equation format with examples”, we will discuss Accounting equation with 7 examples in a Logical manner.
Let’s start..!!
What is an Accounting Equation ?
The accounting equation is the fundamental equation that derives the relationship between the total value of Business Assets with Liabilities and the Owner’s Equity. It is based on a Double entry system of accounting.
In simple, every journal entry will have a dual effect both on the Debit and Credit side of ledger accounts.
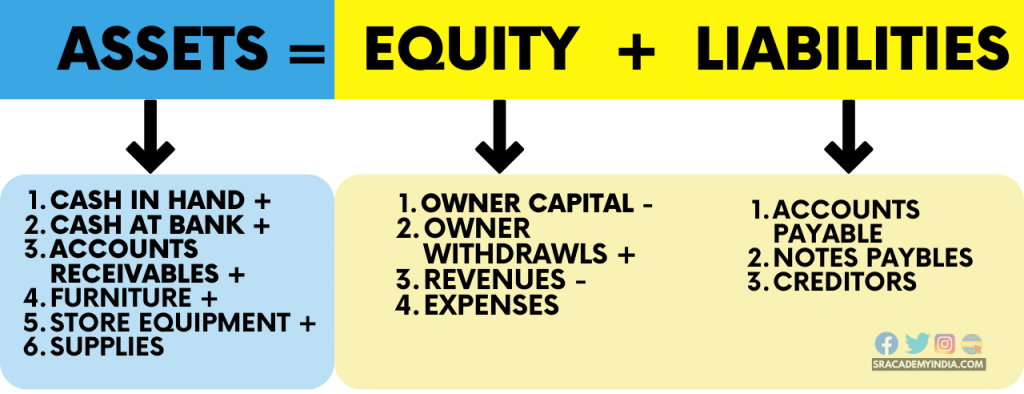
Therefore, the Accounting equation is based on 3 major elements of business.
- Assets (What business Owns)
- Equity (What business Owes to Owners)
- Liabilities (What business Owes to Non-Owners)
1. Assets
Assets are the resources any business enterprise owns or controls. From the assets, the business will generate future benefits either from selling the goods or Services
Eg: If your business bought a Bakery Machine which will produce Cakes and Pizzas. The bakery machine is an Asset to your business and you will generate revenue by selling Cakes and Pizzas.
Not only from goods manufactured but also by rendering services the businesses will generate revenue.
When the bakery machinery is becoming idle for a few days in a month, then you can outsource your facility to other bakers as well to utilize the full capacity of the bakery machinery.
Such services will generate additional revenue for your business by utilizing the idle time in a productive manner.
In such cases, for the goods manufactured / services rendered, the company might receive cash immediately. Then, it will be transferred to the Cash account &
In case the amount is not received immediately but will be received in the near future, then such amount will be transferred to Accounts Receivables or Receivables account.
Here, receivables are the Current assets of the business. And Assets includes both Current Assets and Non-Current Assets. Non-current assets are also called as Fixed Assets.
Non-Current Assets are Assets which are having a useful life of more than 1 year.
Eg: Cars, Buildings, Machinery, etc.,
2. Equity
Equity means the Owner’s capital (or) the Proprietor’s capital brought into the business in the form of Cash. It is called Owner’s Equity.
If money is brought into the business by way of Shares, then it will be called “Equity Share Capital“. While computing the Equity, Net income/ loss of the business should be taken into consideration.
In Simple, Equity means “What the business owes to its Owners”. It can be derived as follows.
“Equity means Assets minus Liabilities“
3. Liabilities
Liabilities means “What a company owes to its Non-owners”.
Eg: Payment to be made to the suppliers for the purchase of the Raw materials for Cakes and Pizzas on a credit basis i.e. Creditors
What is Accounting Equation Formula?
The Accounting Equation formula in broad is as follows.
Assets = Equity + Liabilities
While writing any Journal entry, this accounting equation must be followed.
For each entry, either Assets on the left-hand side may be increased or the equity and liabilities on the right-hand side may be decreased or vice versa.
The more detailed Accounting equation is as follows:
Assets = Owners capital – Owners withdrawals + Revenue – Expenses + Liabilities
What are the Accounting Equation rules of Debit and Credit
To know about the rules of Debit and Credit, you must read the Golden Rules of Accounting.
Examples
Let’s discuss 7 real-life examples which are useful for every business.
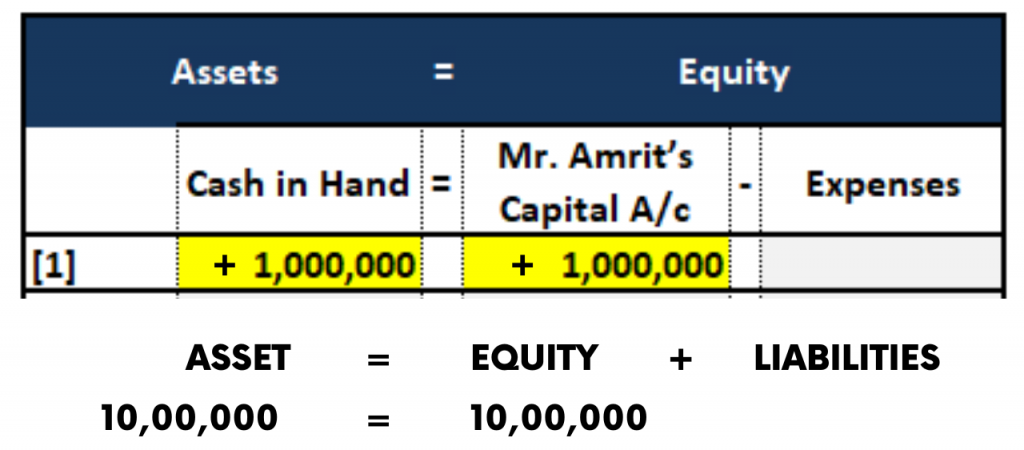
1. Accounting Equation of Capital Investment by the Owner
On 1st January, Mr. Amrit (a sole proprietor) started a textile business in the name of M/s Amrit Handloom Enterprises. The business deals with Manufacturing Men’s clothing and Women’s clothing. Mr. Amrit owns and manages the business and personally invests Rs.10,00,000 cash into the business.
What is the Journal entry and its impact on Accounting Equation?
The Journal Entry for the transaction will be as follows:
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Cash A/c Dr | 10,00,000 | |
| To Mr. Amrit’s Capital A/c | Rs.10,00,000 |
Explanation: Since Mr. Amrit brought Cash into business, the Cash balance is increased. Therefore, the Cash account is debited.
And on the flip side, Since the Capital is brought in by Mr. Amrit, M/s Amrit Handloom Enterprises is liability to pay to Mr. Amrit.
So Mr. Amrit’s Capital a/c is credited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
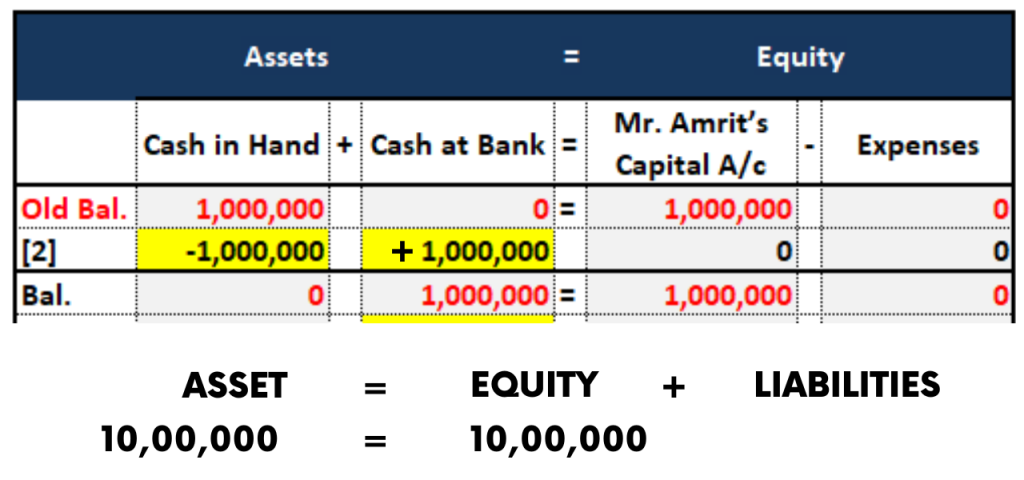
2. Accounting Equation of Cash deposited into Bank
On 2nd January, Mr. Amrit opened a Bank account in the name of M/s Amrit Handloom Enterprises and he deposited Rs.10,00,000 cash in the Bank for day-to-day business activities.
What is the Journal entry and its impact on Accounting Equation?
The Journal Entry will be as follows
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Bank A/c Dr | 10,00,000 | |
| To Cash A/c | 10,00,000 |
Explanation:
Since the Cash is deposited into Bank, the cash is moved out of the business. So Cash a/c is to be credited.
Whereas the Bank balance in the bank is increased due to the Cash outflow from business, therefore it is Debited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
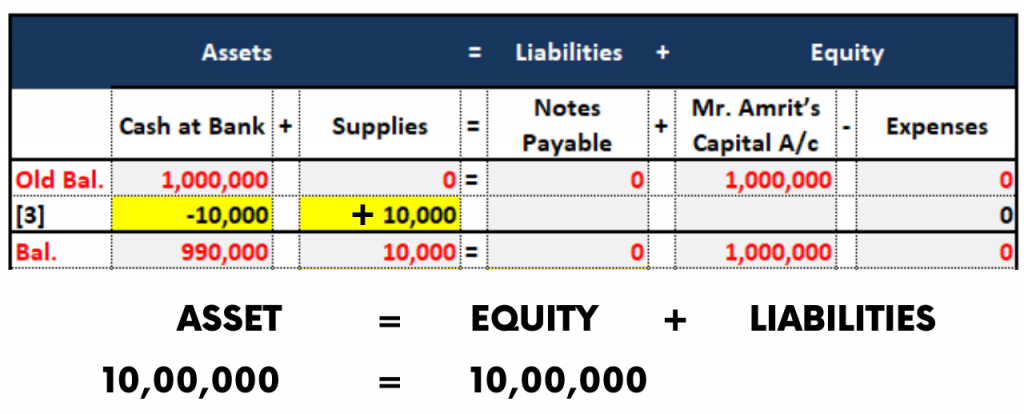
3. Accounting Equation for Purchase of Goods for Cash
On 5th January, Mr.Amrit bought indirect materials of needles Rs.10,000 in the local market by cheque.
The Journal Entry for the transaction will be as follows
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Purchases / Supplies A/c Dr | 10,000 | |
| To Bank A/c | 10,000 |
Explanation:
Due to the purchase of goods “Stock” balance will be increased, So the “Purchases” account is debited which is an “Expense”
And cash goes out of the business i.e. Bank balance is decreasing, So it is credited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
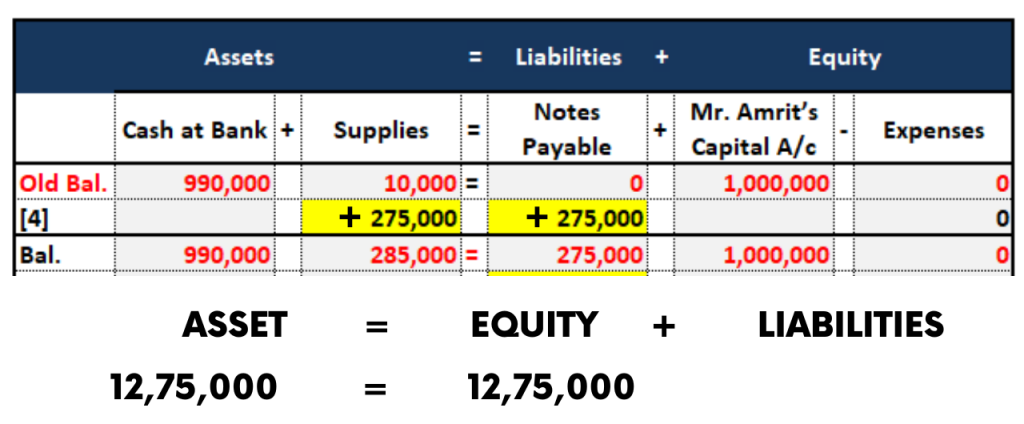
4. Accounting Equation of Purchase of Goods on credit
On 9th January, Mr. Amrit dealt with his friend in Mumbai and purchased clothes for Rs.2,75,000 in bulk for production purposes.
The Journal Entry will be as follows:
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Purchases / Supplies A/c Dr | 2,75,000 | |
| To Creditors / Accounts Payable A/c | 2,75,000 |
Explanation:
Due to the purchase of goods “Stock” balance will be increased, So the “Purchases” account is debited which is an “Expense”
As the goods are purchased on a credit basis, the liability for the business will be increased. i.e. Creditors/ Accounts Payable. So it is credited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
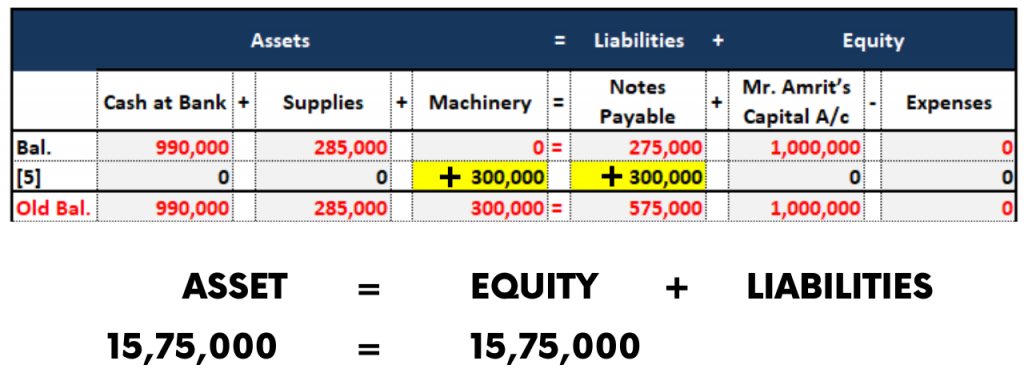
5. Accounting Equation for Purchase of Capital items on credit
On 13th January, Mr. Amrit Purchased a Machinery worth Rs.3,00,000 for production purposes which includes the Transportation cost.
The Journal Entry for the transaction will be as follows
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Machinery A/c Dr | 3,00,000 | |
| To Creditors / Accounts Payable A/c | 3,00,000 |
Explanation:
Due to the purchase of Machinery,”Asset” balance will be increased, So the “Machinery” account is debited.
As the machinery is purchased on a credit basis, the liability for the business will be increased. i.e. Creditors/ Accounts Payable. So it is credited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
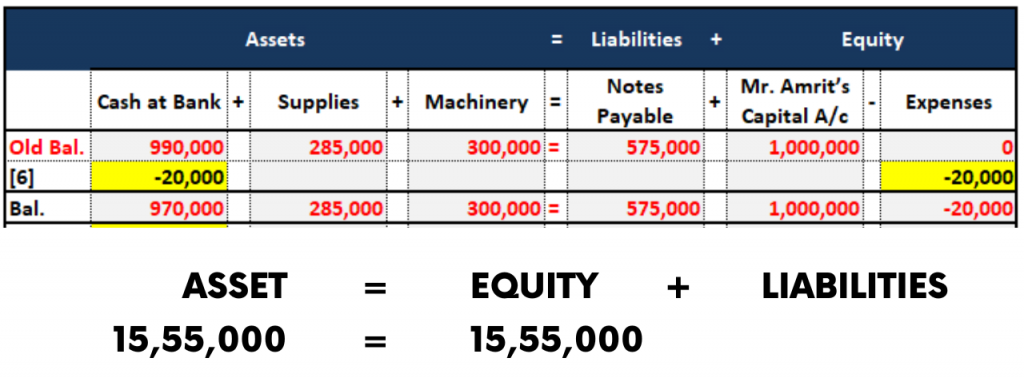
6. Accounting Equation of Rent paid
On 16th January, Mr. Amrit paid rent for the premises of Rs.20,000 by Cheque which will be utilized for production and godown purposes.
The Journal Entry will be as follows
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Rent A/c Dr | 20,000 | |
| To Bank A/c | 20,000 |
Explanation :
Payment of “Rent” is an Expense.
Due to the payment of Rent, expenses will increase. So it is debited.
And also, due to payment by cheque the bank balance will decrease so it is credited.
The Accounting Equation for this transaction is as follows:
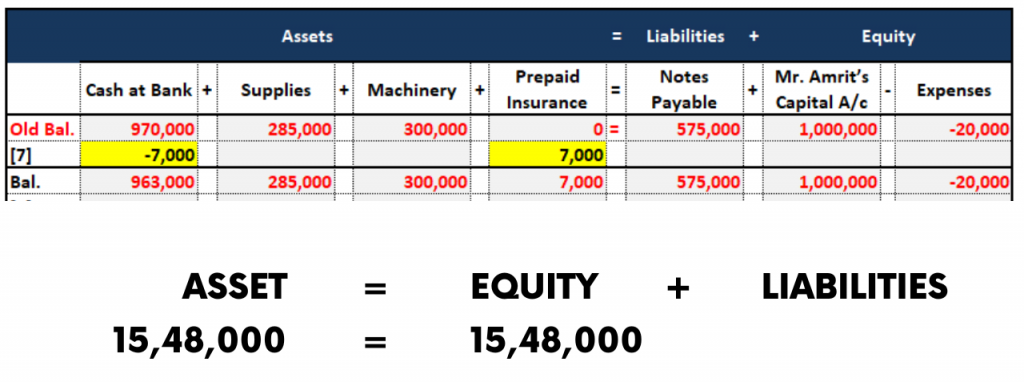
7. Accounting Equation of Prepaid Insurance
Mr. Amrit, On 21st January, took an insurance cover for his business to secure the goods from fire or any other natural calamity. The premium for such an insurance policy is Rs.7,000 which covers a period of 12 months .
The Journal Entry for the transaction will be as follows
| Particulars | Dr (Rs.) | Cr (Rs.) |
| Prepaid Insurance A/c Dr | 7,000 | |
| To Bank A/c | 7,000 |
Explanation:
Whenever you pay for expenditures in advance is called Prepaid Expenses. And it is an Asset.
Therefore, Prepaid Insurance is an Asset. Since its balance is increasing, it is debited.
And also due to payment by cheque, the bank balance will decrease so it is credited.
The accounting equation for this transaction is as follows:
Read More: 3 Powerful Accounting Terms with Examples
Understanding the accounting equation is a very crucial step in estimating how the funds are coming into the business and how these are catered for various requirements of the business. I hope you understood the “Accounting Equation format with Examples” concept.
Your feedback will help us to improve. So please Comment “GOOD” if you like the article and it really encourages us to bring lots of new content. Also, share this article with your Friends & Family…
Thanks for reading..!!!