In this article, I am going to discuss about “6 Liquidity and Solvency Ratios” which would be helpful in analyzing comapny’s Financial statements.
We also compiled the Liquidity Ratios as well as Solvency ratios for a better understanding of the concept.
Let’s get started..!
Liquidity Ratios
Liquidity ratios help to identify & ascertain whether the company has enough working capital to pay off its short-term obligations.
1. Current Ratio
Meaning of Current ratio
The current ratio measures whether the business has enough current assets to pay its current liabilities. The current ratio refers to current assets to current liabilities.
Formula of current ratio
The formula of the current ratio is

“Current assets” includes
Inventories
+ Sundry debtors
+ Accounts Receivables
+ Cash/Bank balances
+ Short-term Investments
+ Short-term Loans & advances
+ Any other current asset
“Current liabilities” includes
Creditors
+ Bank Overdraft
+ Cash credit
+ Short-term Loans
+ Outstanding expenses
+ Proposed dividend
+ Provision for Taxation + Any other current liability
Ideal Current ratio
The Idle Current ratio is 2:1
Current ratio interpretation
- Higher Current ratio > Indicates Heavy investment in Current Assets which means Under utilization of resources.
- Lower Current ratio > Indicates the Company is not in a position to pay off short-term debts.
Read also: What everyone must know about 40 Basic Accounting Terminology
2. Quick Ratio
Quick ratio meaning
The quick ratio measures the business’s capacity to meet its short-term obligations. It is also defined as Assets that are quickly convertible into cash. i.e. Most liquid assets like Cash, Cash equivalents, Marketable Securities etc., It is also called as “Acid-Test ratio”.
Quick ratio formula
The formula of the Quick ratio is

“Quick assets” includes
Total current assets
(-) Closing Inventory
(-) Prepaid expenses
“Current liabilities” includes
Creditors
+ Bank Overdraft
+ Cash credit
+ Short-term Loans
+ Outstanding expenses
+ Proposed dividend
+ Provision for Taxation
+ Any other current liability.
Ideal Current ratio
The Idle Quick ratio is 1:1
Quick ratio interpretation
- Higher Quick ratio > Indicates very risky.
If the quick ratio is 1 or higher, it means that the corporation has enough liquid assets to cover its immediate liabilities. On the other side, a very high quick ratio isn’t always a positive thing. - Lower Quick ratio > Indicates unnecessary use of resources in less profitable short-term investments
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when quick ratio is less than 1?
If the company’s quick ratio is less than1, then the company is unable to satisfy its short-term obligations.
Is a higher quick ratio better or worse?
A higher quick ratio is always good.
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios measures, how better a company’s cash flows can recover its long-term debts.
i.e. Ability to pay Long-term debt obligations.
Solvency ratios help to assess the financial health of the company and also assess the company’s debt defaulting situation which are long term in nature.
3. Debt-Equity Ratio
Debt – Equity ratio Meaning
Debt- Equity ratio measures the relationship between Long-term debt and Equity which evaluates the Financial leverage of a company. It also calculates the extent to which it can cover the debt.
It represents the company’s finances are met equally by debt and equity. It evaluates the proportion to which an organization is able to finance its operations by Debt rather than its own resources.
Debt – Equity ratio Formula
The formula of the Debt- equity ratio is

“Long-term Debt” includes Total outside liabilities
“Shareholder’ funds” includes
Equity Share capital
+ Preference Share capital
+ Reserves and Surplus
+ Money received against share warrants
(or)
Non-current assets + Working capital – Non-current liabilities
“Working Capital” means Current assets – Current Liabilities
Ideal Ratio
The Idle Debt- Equity ratio is 2:1
Debt – Equity ratio Interpretation
- Higher Debt- Equity ratio –> A ratio of more than 1 indicates that the company’s financing is done more by debt rather than its equity.
Indicates Risky i.e. Less protection for Creditors. It represents the firm’s difficulty to meet its external obligations. - Lower Debt- Equity ratio > Indicates More security for Creditors. A ratio of less than 1 indicates that a company’s finances are more by equity than through debt.
4. Proprietary Ratio
Proprietary ratio Meaning
It measures the relationship between money invested by the proprietors into the business and the total value of assets the company owns. i.e. relationship between Shareholder’s funds to Net assets.
It is also called a “Equity ratio” or “Shareholder’s Equity ratio” or “Networth ratio”
Proprietary ratio formula
The formula of the Proprietary ratio is

“Shareholder’ funds” includes
Shareholders’ Funds = Equity Share capital + Preference Share capital + Reserves and Surplus + Money received against share warrants
(or)
Non-current assets + Working capital – Non-current liabilities
“Working capital” means Current assets – Current Liabilities
“Capital employed” includes Total assets – Current Liabilities
Ideal Ratio
The Idle Proprietary ratio is 0.5:1
Proprietary ratio Interpretation
- A higher Proprietary ratio > indicates the organization has sound financial position
- Lower Proprietary ratio > indicates long-term loans and other obligations are less secure and the company can lose their money.
5. Total Assets to Debt Ratio
Total assets to Debt ratio meaning
It represents the total assets of a company are expressed in relation to its Long term debts. It established the relationship between total assets and long-term loans.
Total Assets to Debt ratio formula
The formula of the Total assets to Debt ratio is
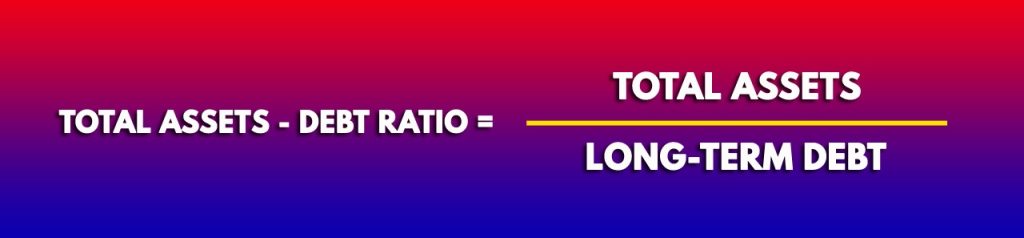
“Total assets” includes Non-current assets + Current assets“
“Long-term Debt” includes Total outside liabilities
Ideal Ratio
The Ideal Total assets to Debt ratio is 0.5:1
Total Assets to Debt ratio Interpretation
- Higher Total assets to Debt ratio > indicates more security to lenders of long-term loans
- Lower Total assets to Debt ratio > indicates less security to lenders of long-term loans
6. Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest coverage ratio Meaning
It represents the company’s ability to meet the interest on its outstanding debt.
In other words, the interest coverage ratio is one of the financial ratio that attempts to measure how easily an organization can pay its interest expenses on outstanding debt.
Interest coverage ratio Formula
The formula of the Interest coverage ratio is

Ideal Ratio
The Interest coverage ratio of 1.5 is the minimum acceptable level.
Interest coverage ratio Intrepretation
- Higher Interest coverage ratio > indicates the company’s ability to clear the debt
- Lower Interest coverage ratio > indicates the company is unable to pay its interest on the debt.
Also read: Golden rules of Accounting – An easy understanding
I hope you understood the “6 Liquidity and Solvency Ratios” concept.
Please Comment “GOOD” if you like the article and it encourage us. Also share this article to your Finance related Friends & Family…
Thanks for reading..!!!
Disclaimer: The materials provided herein are solely for information purpose. No attorney-client relationship is created when you access or use the site or the materials. The information presented on this site does not constitute legal or professional advice and should not be relied upon for such purposes or used as a substitute for legal advice from an attorney licensed in your state.
Also, every effort has been made to avoid errors or omissions in this material. In spite of this, errors may creep in. Any mistake, error or discrepancy noted may be brought to our notice which shall be taken care of in the next edition. In no event the author or the website shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from or arising out of or in connection with the use of this information.