Whether you run your own Sole proprietor business or You might have a Partnership business with partners, then, how would you assess whether your Business has scored Profit or debacle of Loss?
To assess whether Profit is earned or Loss is incurred, you should first understand a statement i.e. the “Profit and Loss account” or “Statement of Profit and Loss”.
Let’s get started..!!
1. Profit and Loss Account Meaning
A Profit and Loss account is a Statement that summarizes the Revenues, Costs, and Expenses incurred for a particular accounting period.
It records all Incomes and Expenses of the business. It is prepared based on accounting principles of Revenue recognition, Accruals, Matching, etc.
Every business enterprise whether it is a Sole proprietor or a Partnership Firm or a Company, needs to maintain a Profit and Loss account. The main reason to prepare it is to find the correct results for the business.
The Profit and Loss account will be prepared to assess whether the business has earned a Profit or occurred a Loss over a period of time. It is usually from 01st April to 31st March of every year.
A profit & Loss Account is also known as an “Income Statement” or “Statement of Profit & Loss”
2. Why the Profit and Loss account will be prepared?
There are 2 reasons to prepare a Profit and Loss account –
1. To ascertain Profit or Loss made by the business enterprise
2. For Statutory compliance ( For compliance with the Companies Act, Partnership Act, or any other governing law)
3. Profit and Loss Account Format for Sole Proprietor & Partnership Firms
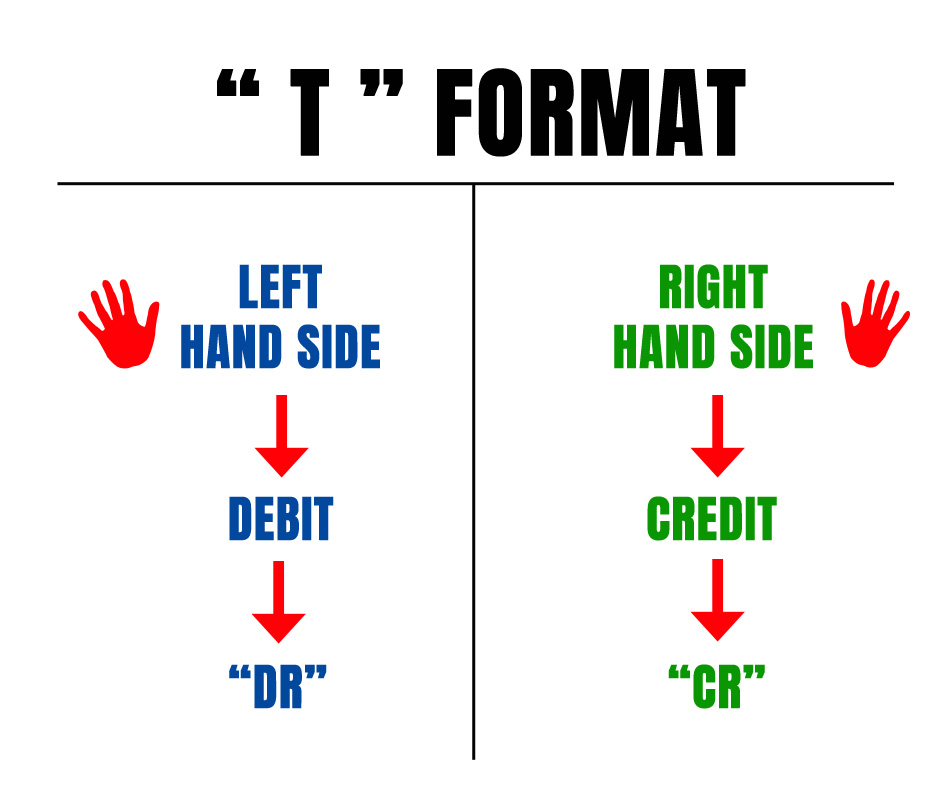
For Sole proprietors & Partnership firms, there is no specific format for the preparation of the Profit and Loss account. But usually, the Profit and Loss account will be prepared in a “T” Shape. i.e. in Horizontal Format.
Horizontal format (“T” Shape)
Before preparing the Profit and Loss account for your Sole proprietor business or for your Partnership firm, a “Trading account” will be prepared.
The Trading account records all the Expenses directly related to Manufacturing / Trading concerns for the purpose of ascertaining Gross Profit or Gross Loss for a particular period.
The “T” shaped Profit and Loss account has 2 sides.
1. Debit
2. Credit
The horizontal format of the Trading, Profit, and Loss account will be as follows for Sole proprietors & Partnership firms.
In the books of
M/s……………..
Trading, Profit and Loss account for the period ending 31st Mar,xxxx
Dr Cr
| Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Particulars | Credit (Rs.) |
| To Opening stock | xxx | By Sales Less: Returns | xxx |
| To Purchases Less: Returns | xxx | By Closing stock | xxx |
| To Direct expenses | By Gross Loss c/d (Balance figure) | xxx | |
| – Inward freight | xxx | ||
| – Factory rent | xxx | ||
| – Wages et., | xxx | ||
| To Gross Profit (Balance figure) c/d | |||
| xxx | xxx | ||
| To Gross Loss (Balance figure) b/d | xxx | By Gross Profit (Balance figure) b/d | xxx |
| To Administrative expenses | By Other incomes | ||
| – Salaries | xxx | – Discount received | xxx |
| – Office rent | xxx | – Commission received | xxx |
| – Power and Fuel | xxx | By Non- Trading Incomes | |
| – Insurance | xxx | – Bank interest | xxx |
| – Audit fees | xxx | – Rental incomes | xxx |
| – Legal fees | xxx | – Dividend income | xxx |
| – Repairs & Maintenance | xxx | By Abnormal gains | |
| To Selling & Distribution expenses | xxx | – Profit on sale of Machinery | xxx |
| To Interest & Finance charges | – Profit on sale of Investment | xxx | |
| – Interest on Loan | xxx | By Net Loss (Transferred to Capital Accounts) | xxx |
| – Bank charges | xxx | ||
| Abnormal Losses | |||
| – Loss on sale of Machinery | xxx | ||
| – Loss by fire | xxx | ||
| To Depreciation on | |||
| – Plant & Machinery | xxx | ||
| – Buildings etc., | xxx | ||
| To Net Profit (Balance figure) [Transferred to Capital Accounts] | xxx | ||
| xxx | xxx |
4. Profit and Loss Account Format for Companies
In the case of Companies, the Statement of Profit and Loss account is to be prepared as per Schedule III of the Companies Act,2013.
Following is the Format of the Statement of Profit and Loss account as per Schedule III.
PART II – STATEMENT OF PROFIT AND LOSS
Name of the Company…………………….
Profit and loss statement for the year ended 31st March, XXXX
(Figures in Rupees)
| Particulars | Note No. | Figures as at the end of the previous reportingperiod | Figures as at the end of the previous reporting period | |
| I. | Revenue from operations | xxx | xxx | |
| II. | Other income | xxx | xxx | |
| III. | Total Revenue (I + II) | xxx | xxx | |
| IV. | Expenses: | |||
| > Cost of materials consumed | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Purchases of Stock-in-Trade | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Changes in inventories of finished goods work-in-progress and Stockin-Trade | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Employee benefits expense | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Finance costs | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Depreciation and amortization expense | xxx | xxx | ||
| > Other expenses | xxx | xxx | ||
| Total Expenses | xxx | xxx | ||
| V | Profit before exceptional and extraordinary items and tax (III-IV) | xxx | xxx | |
| VI. | Exceptional items | xxx | xxx | |
| VII. | Profit before extraordinary items and tax (V – VI) | xxx | xxx | |
| VIII. | Extraordinary items | xxx | xxx | |
| IX. | Profit before tax (VII- VIII) | xxx | xxx | |
| X. | Tax expense: (1) Current tax (2) Deferred tax | xxx xxx | xxx xxx | |
| XI. | Profit (Loss) for the period from continuing operations (VII-VIII) | xxx | xxx | |
| XII. | Profit/(loss) from discontinuing operations | xxx | xxx | |
| XIII. | Tax expense of discontinuing operations | xxx | xxx | |
| XIV. | Profit/(loss) from Discontinuing operations (after tax) (XII-XIII) | xxx | xxx | |
| XV. | Profit (Loss) for the period (XI + XIV) | xxx | xxx | |
| XVI. | Earnings per equity share:( 1) Basic (2) Diluted | xxx xxx | xxx xxx | |
5. Types of Profit and Loss (P&L) Statements
A Profit and Loss account can be prepared in 2 methods
- Cash basis
- Accrual basis
Method 1 – Cash Basis
Under the Cash basis, the Revenues and Expenses will be recognized, when the actual receipts or payments are made.
Method 2 – Accrual Basis
The accrual basis of accounting is one of the methods of recording accounting transactions in the books of accounts.
Under an Accrual basis, Revenue will be recognized when the revenue is earned (Not when received) and Expenses will be recognized as and when accrued (Not at the time of payment)
6. Profit and Loss Account Example
For Sole proprietor & Partnership firms
Illustration 1:
M/s Harsha Enterprises provides the below Revenues & Expenses details for the year ended 31st March, 2022
Salaries Rs.4,65,000, Discount allowed Rs.4,500, Discount received Rs.6,000, Bank Interest Rs.9,500, Loss by theft Rs.19,000, Depreciation on Plant Rs.23,000, Gross Profit Rs.3,28,500, Power and fuel charges Rs.45,000, Printing & Stationery Rs.2,525, Interest on Loan Rs.85,000, Consultancy charges Rs.35,000, Audit fees Rs.50,000, Legal fees Rs.25,000, Postage charges Rs.1,500, Telephone charges Rs.6,500
Required:
Prepare the Profit and Loss account of M/s Harsha Enterprises for the year ended 31st March 2022.
Solution:
In the books of
M/s Harsha Enterprises
Trading, Profit, and Loss account for the period ending 31st Mar, 2022
Dr Cr
| Particulars | Debit(Rs.) | Particulars | Credit(Rs.) |
| To Salaries | 1,65,000 | By Gross Profit | 5,28,500 |
| To Power and fuel charges | 45,000 | By Bank Interest | 9,500 |
| To Interest on Loan | 85,000 | By Discount received | 6,000 |
| To Consultancy charges | 35,000 | ||
| To Printing & Stationery | 2,525 | ||
| To Audit fees | 50,000 | ||
| To Legal fees | 25,000 | ||
| To Depreciation on Plant | 23,000 | ||
| To Discount allowed | 4,500 | ||
| To Loss by theft | 19,000 | ||
| To Postage charges | 1,500 | ||
| To Telephone charges | 6,500 | ||
| To Net Profit | 81,975 | ||
| , | 5,44,000 | 5,44,000 |
I hope you understood the “Profit and Loss Account” concept.
Please Comment “GOOD” if you like the article and it encourages us. Also, share this article with your Finance related Friends & Family…Thanks for reading..!!!
———————————————————End——————————————————————
Disclaimer: The materials provided herein are solely for information purpose. No attorney-client relationship is created when you access or use the site or the materials. The information presented on this site does not constitute legal or professional advice and should not be relied upon for such purposes or used as a substitute for legal advice from an attorney licensed in your state.
Also, every effort has been made to avoid errors or omissions in this material. In spite of this, errors may creep in. Any mistake, error or discrepancy noted may be brought to our notice which shall be taken care of in the next edition. In no event the author or the website shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from or arising out of or in connection with the use of this information.